Introduction
McDonald’s is a nostalgic component of America 🇺🇸 and a pioneer of fast food operations and real estate ventures, as depicted in the 2016 film, The Founder, about Ray Kroc. As a kid I traveled to different McDonald’s across the east coast and noticed a difference in the classic hamburger preparation for adding mustard (i.e. in Maryland and not in Upstate New York). After some Google research, I noticed others had documented the regional differences in the use of mustard and but no aggregated data set existed detailing which McDonald’s added mustard to their hamburgers.

I hypothesized that these deviations in food prep could be identified from yelp.com reviews. The process below explains the approaches I took to gather data from the web with the yelp API and the development of a shiny web application which detects string patterns in reviews for the keyword ‘mustard’ for a specific McDonald’s.
API Process
This script highly references Jenny Bryan’s yelpr example!
library(yelpr) # devtools::install_github("jennybc/ryelp")
library(httr)
library(stringr)
library(purrr)
# 1. Create an application on the [Yelp developers site](https://www.yelp.com/developers/v3/manage_app) and agree to the Terms and aggreements
## Set your credentials as environment variables.
Sys.setenv(YELP_CLIENT_ID='**************')
Sys.setenv(YELP_SECRET='*****************************')
# 2. search for businesses by creating an app
yelp_app <- oauth_app("yelp", key = Sys.getenv("YELP_CLIENT_ID"),
secret = Sys.getenv("YELP_SECRET"))
# authenticate an endpoint
## https://www.yelp.com/developers/documentation/v3/authentication
yelp_endpoint <- oauth_endpoint(NULL,
authorize = "https://api.yelp.com/oauth2/token",
access = "https://api.yelp.com/oauth2/token")
# 3. Get an access token: Just enter anything for the authorization code when prompted in the Console of RStudio
token <- oauth2.0_token(yelp_endpoint, yelp_app,
user_params = list(grant_type = "client_credentials"),
use_oob = T) # make this arg TRUE when interactive
# 4. Create a url to make calls to the business search endpoint: The parts of the url include the endpoint and the query search parameters after the **?**
(url <-
modify_url("https://api.yelp.com", path = c("v3", "businesses", "search"),
query = list(term = "McDonalds",
location = "Hartford, CT", limit = 10)))
# 5. Retrieve info from the server with the `GET` verb: HTTP response verbs enable the client to send us back data on: status, headers, and body/content. Available verbs include **`GET`ting** data from the server, **`POST`ing** new data to the server, **`PUT`** new data to update a partial record and **`DELETE`ing** data.
response1 <- GET(url, config(token = token))
# was this api request successful?
## HTTP status codes consist of 3 digit numeric codes for status (1xx is information, 2xx is success, 3xx is redirection, 4xx is client error, 5xx server error).
http_status(response1)
# what type of format does the data come back with?
response1$headers$`content-type`
# 6. Return some content with geolocation data, business info & categories
ct2 <- content(response1)
## create an object with resturant name and id for further calls
biz_info <- ct2$businesses %>%
map_df(`[`, c("name", "id", "phone", "review_count"))
biz_info %>% knitr::kable()
# 7. Get business reviews: After getting a specific McDonald's `id` restructure the url as an individual value and secondly creating a function to create a data.frame with urls for each business from the search endpoint.
url_id <- modify_url("https://api.yelp.com",
path = c("v3", "businesses","mcdonalds-glastonbury", "reviews"),
query = list( locale = "en_US"))
# 8. Retrieve response data on up to 3 reviews for the specific McDonald's
response2 <- GET(url_id, config(token = token))
content2 <- content(response2)
# Detect for string of 'mustard'
content2$reviews %>%
map_df(`[`, c("text")) %>%
str_detect("mustard")
The purrr version to check multiple restaurant text reviews for the string ‘mustard’.
# create a function to structure the urls with the business id
url_id_f <- function(id) {
modify_url("https://api.yelp.com", path = c("v3", "businesses", id, "reviews"),
query = list( locale = "en_US"))
}
# create a df which maps the url function of all the restaurants
biz_reviews <- data.frame()
biz_reviews <- map_chr(biz_info$id, url_id_f) %>%
data.frame(url = .)
biz_reviews$url <- as.character(biz_reviews$url)
# Get each url for the request
response3 <- map(biz_reviews$url, GET, config(token = token))
response3 %>% map_df(`[`, "status_code") == 200
# loop through each restaurant's 3 reviews and extract the text and detect the presence of the string 'mustard'
for (idx in 1:length(response3)) {
mcd <- response3[[idx]]
ct <- content(mcd)
print(ct)
result <- ct$reviews %>%
map_df(`[`, c("text")) %>%
str_detect("mustard")
print(result)
}
Learnings & Gotchas
The non-premium API access only includes up to 3 reviews and only a sample of the full text, leaving obvious gaps when trying to detect the keyword ‘mustard’ and contingent on enough reviews which details 🍔 preparation.
In trying to create and publish a shiny application that wraps this code, I came up with errors given that OAuth2.0 grants access to users 👩 and not applications 💻. However here is a screenshot of the script above developed into an interactive shiny application to search for any [city, state] and the gist of the code if your interested in running a local version.
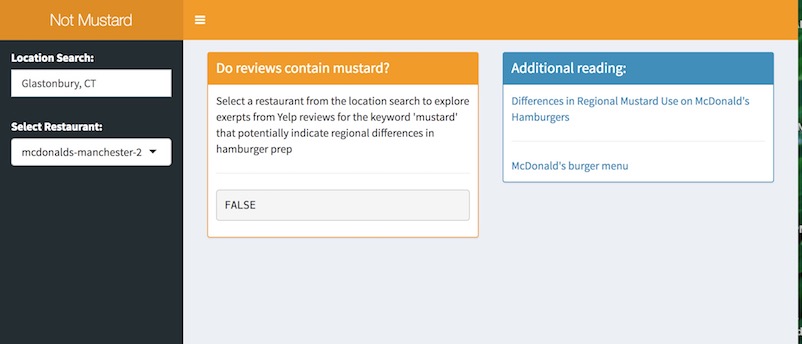
The name of this shiny app is a nod to Silicon Valley’s Not Hotdog application.
Cover Image source: https://www.mcdonalds.com/us/en-us/about-us.html